21)C PROGRAM TO REVERSE A NUMBER AND A STRING
(A)REVERSE A NUMBER
LOGIC:-
(A)REVERSE A NUMBER
LOGIC:-
- take any number from user which you want to reverse
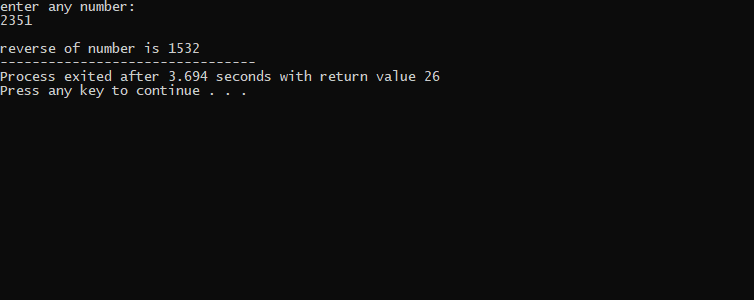
- using "/" to find the quotient i.e let num=2351 now divide num/10 = 235.Next using "%" to find the remainder i.e num%10=1 store it.
- again divide the new num which is 235 now we have new num after divide is =23 and remainder is 5. so apply logic that after 1 , 5 is come and so on...
- reverse=reverse*10+remainder // this code create a reverse.
EXAMPLE:-
(B)REVERSE A STRING:
LOGIC:- we can reverse string from many ways by using string reverse function(strrev()), without strrev() , by using pointers etc.Here 2 ways are given.
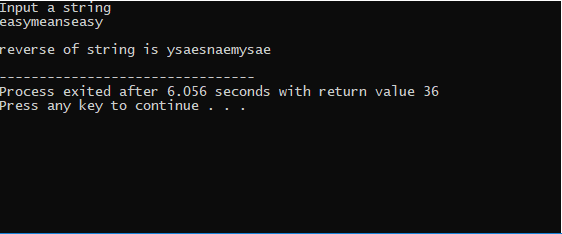
EXAMPLE 1 :- BY USING STRREV FUNCTION
EXAMPLE 2 :- WITHOUT USING STRREV FUNCTION
- first declare two empty character array(similar to string).
- input string in one array
- now find the length of the input array.
- now using a loop where first character of input array is insert at the last of second array and so on
- now we have a reverse of the string
NOTE:- WE ALSO FIND THE LENGTH OF STRING USING FUNCTION STRLEN().
(C)BY USING RECURSION:
LOGIC:- Recursion means a function call itself.So we create a function which call itself.In this function we write the code to reverse the string
EXAMPLE:-
TASK:"""TRY WITH POINTER""" WHERE YOU CAN USE SWAPPING TECHNIQUE




Comments
Post a Comment